How do you Patch Drupal?
One day there will be a day when you need to patch Drupal or probably more likely a contributed Drupal module. When that day comes it may seem a daunting task, especially for someone new to working directly with code who doesn't usually have to. Well, I am here to help and to tell you that your best bet is to use the patch utility that is part of Linux. Even though there are also a few Git commands you can use, I have only used the patch command for the last 5-plus years and it works so for now I will stick with it. But if you feel the urge you can check Drupal.org for information on using Git to apply a patch.
I've found the Linux Patch command to be excellent and have not needed to use other methods. Recently I used the GitLab diff to make a patch and that was nice so I guess in time I will move to Git commands. That said, if you are just starting out and only want to patch and not contribute for the time being, then the Linux command is all you'll need.
You could obviously manually apply the patch by reading the patch file and finding the lines to delete and add. I have done this before and it is something I suggest you do once as it gives you an insight into how the patch is formatted which will add to your understanding. Below is a sample patch for the Contact Storage permission issue.
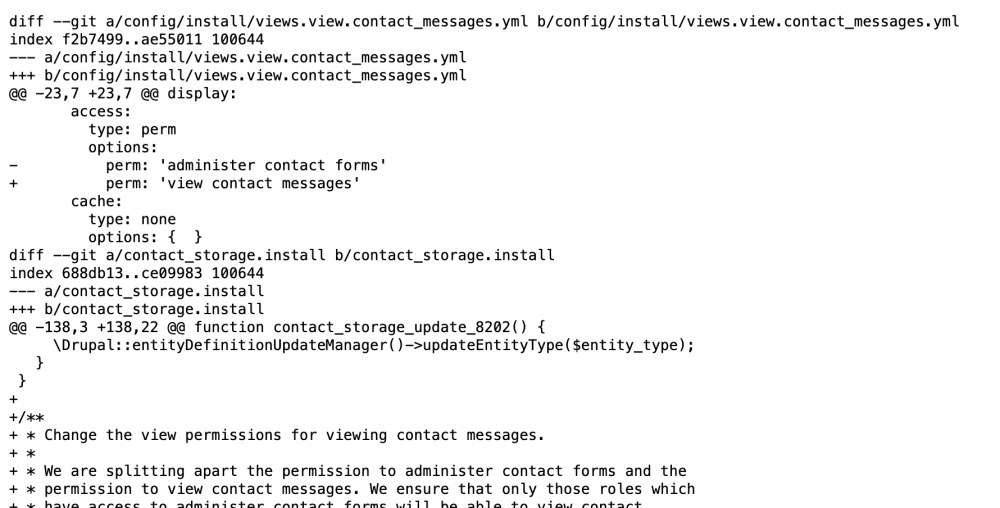
You can see the file or files that are patched and the lines, then you can see the + and - next to the line that is either added or removed respectively. The patch will include the few lines before which are probably used in the operations to locate the correct place to add or delete the modifications. Patches sometimes patch more than one file as in the case of this one.
Should you patch?
The simple answer to this is yes. If you have the issue that the patch fixes, then you should apply the patch on a development instance or branch of your application and test it. You can then add a note to the issue saying you have tested the patch and it works. If need be you could change the issue to Reviewed & tested by the community (RTBC). You should also subscribe to the issue so that you are kept up to date with the issue and then when it is released in the stable version of the code you can document that the patch is no longer needed for your application. Yes, you should keep a document of what you have patched so that when updating you know that it may need to be reapplied if the patch is not included in the release.
Let's Patch!
As I wrote I use the Linux patch command so let's use that. Fire up your CLI, I use the Terminal that comes with Mac. You first need to be in the directory of the module you are wanting to patch. So looking at the above patch you need to be in the contact_storage root directory as all the paths are shown as relative to the patch file. You will also need to have the wget tool installed on your system so if you don't have it you will need to add that too.
Once you have cd'd into the directory using your favourite CLI tool and have wget installed you are reading to go. Below are the steps with a few notes.
Download and Apply a patch
$ cd <directory>
$ wget https://www.drupal.org/files/issues/multiselect-fix-paragraph-inline-entity-form-2672222-6.patchDry run
$ patch -p1 --dry-run < multiselect-fix-paragraph-inline-entity-form-2672222-6.patchApply
$ patch -p1 < multiselect-fix-paragraph-inline-entity-form-2672222-6.patchReverse use -R flag
Reverse Dry run
$ patch -p1 --dry-run -R < bulk_field_editting_after_bulk_uploading-2818683-21.patchReverse Apply
$ patch -p1 -R < bulk_field_editting_after_bulk_uploading-2818683-21.patchCheck for Database updates
Check whether there are database updates, you might be able to see this in the file, or the easiest way is to run the updates either using the UI or Drush. Both these methods will return a message either way and then you can test it.
Testing and reporting
Now you can test that the patch works with your particular set-up. Hopefully, it does and you can report a successful use. If it doesn't, however, you should also report that it doesn't apply cleanly, maybe you have a slightly different configuration and the information might be useful for the maintainers. If it doesn't apply cleanly you can use the reverse command and then also check you are using exactly the same version of the module. Sometimes the patch is for the dev version or is for a new version of Drupal and hasn't been re-rolled for the version you are using. In that case install the same version of the module, for example, if it says dev version, install that version and test.
It's really up to you how much you report, applied to the 1.1 version and it didn't work but applied to dev and works as advertised, thanks! It is also up to you whether you go further and start to use the Git command by checking out the linked article above. Whatever your decision I can say with 100% confidence that the Linux patch command with wget works, it has served me well, and I hope it can serve you well too!
So that's it for to patch or not to patch. I hope you learnt something. If you did why not sign up for the Front-end dev and design newsletter? Nuggets of interesting stuff I promise. Until next time, seize the day!