This is one of the major reasons why Drupal shines. Let's look a little closer.
Every piece of content is a content entityN5 and will belong to an entity type. The main entity type is possibly the content item type (which creates nodes) but other entity types play a big part in structuring a site built using Drupal.
Content entities are items of content data that can be made of settings, such as published and promoted, and content such as text, images, or files. Content entities can be created by core or by a module.
Entity type
Content entities belong to an entity type. There are 8 entity types that ship with Drupal 9 of which 7 are enabled by default. The 8th entity type is Media and this can be installed and configured after installing your Drupal 9 site.
These entity types have different purposes and displays. The entity types that content entities can be created from are:
- Content Item types
- Comment
- Custom Block
- Taxonomy term
- Users Profile
- File
- Contact form
- Media
Media comes with Drupal but you need to set it up, it is a powerful way to manage and make all your media reusable entities. I wrote a quick start guide which currently sits at Drupal 9 Media (https://designkojo.com/drupal-9-media) and I will cover it again as part of the image management and rendering section.
Entity sub-types
Most Entity types can be divided into entity sub-types which are also called bundles.
The most obvious illustration of this is the content type which by default has a page type and an article type (and book type99). All entities of content item entity type have the same settings available by default but can be configured differently for default publishing settings.
Entity Types are managed the same as illustrated. However, you can add any field you want to entity types to make them unique.
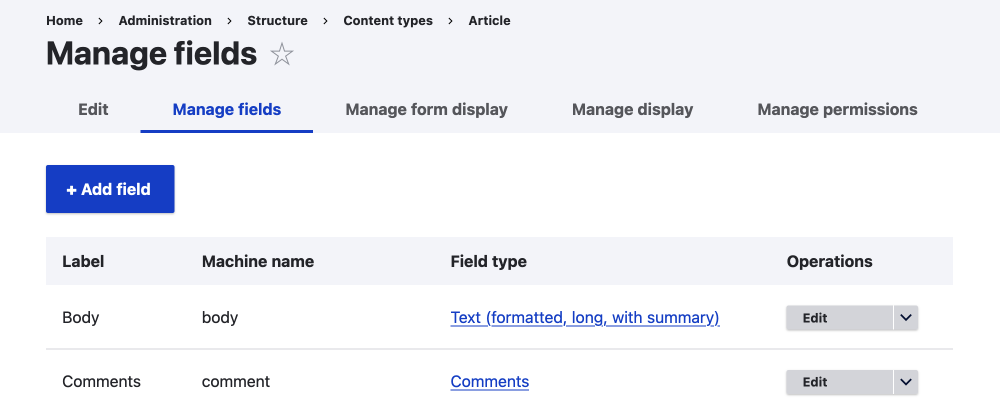
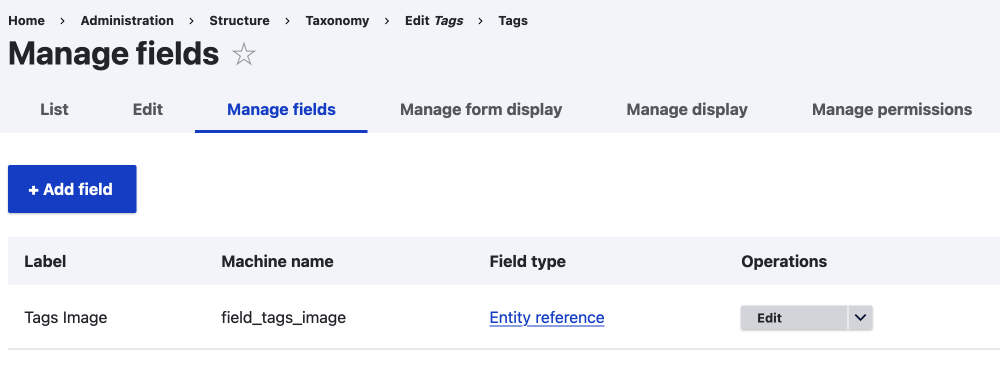
Fields
The most basic building block of a Drupal site.
Entity types are made of fields, some are system fields or option settings and some are content fields. You can add content fields to any entity type you want at a click of a button.
All data types are represented and fields can be anything from boolean checkboxes, email addresses, text, numbers, reference fields, or uploaded images or files.
As mentioned fields have settings that allow all fields to be configured uniquely.
Advanced
Entity Types exposed as Fields
Some entity types create fields such as comments, this is a powerful concept where an entity type can be exposed as a field making it easy to create complex combinations of fields in one field.
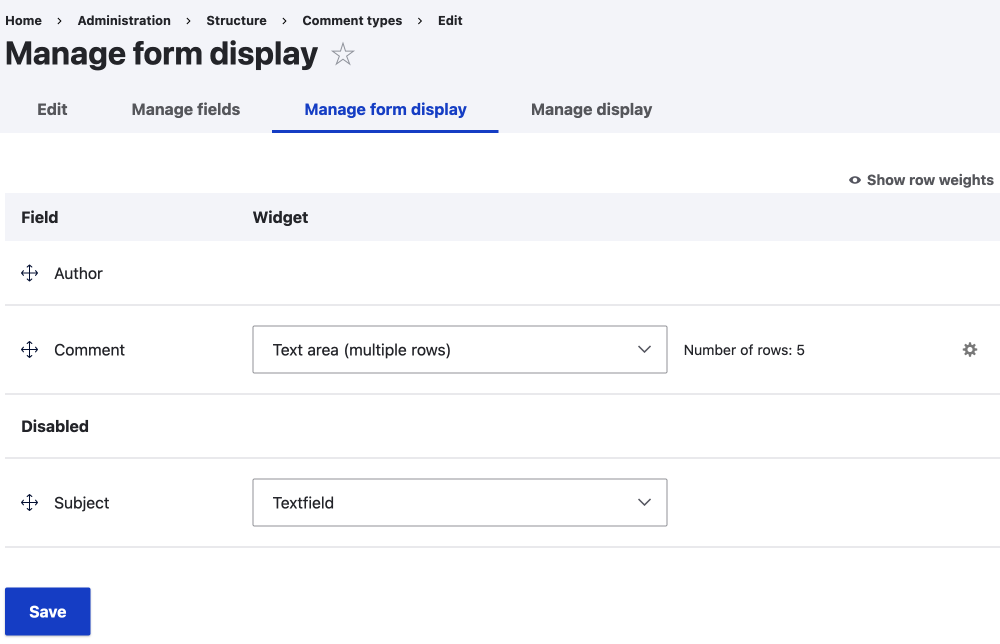
Reference Fields
You can add reference fields to any entity type; taxonomy and comments are good examples of this.
Due to the way data is stored and managed, with a reference field and Views6 you can easily make a relationship on any data field in the Views UI. This makes it easy to get field data from one piece of content and add it to another piece of content.
6Building lists, product cards, or collections of fields with Views
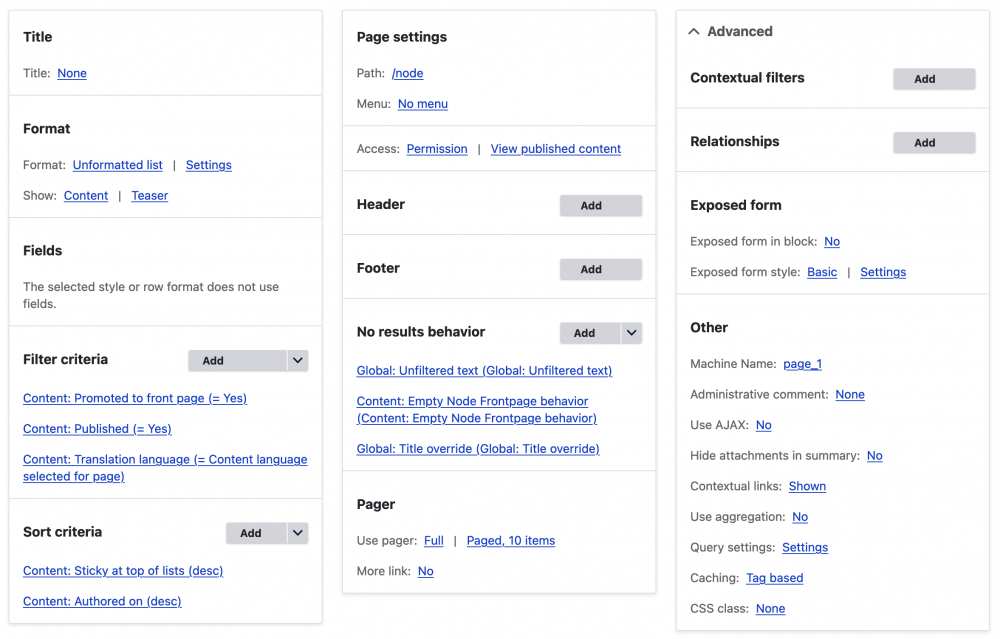
I will mention Views here as it allows you to quickly make listing pages of your entities even though it deserves a section of its own.
Views is a powerful view builder. With views, you can build complex combinations of fields using a point and click interface. Views module has been around since the early days of Drupal. When I first got started with Drupal 6, Views was one of the must-have modules that every site should install. Thankfully for us, it has been part of Drupal core since Drupal 8.
Understanding this basic concept of entities and fields and how well Drupal does this at its core will hopefully make you understand why Drupal is a powerful system and solution for almost any website or application. Its core strength is the way it stores and allows access to data and you can get all of this by installing Drupal and learning some basic concepts.